Research Experience - Comparing Statistics vs Machine Learning
There are so many terms regarding the field of Statistics and Data Science. We often heard Statistics, Data Mining, Machine Learning, Big Data, etc. It especially confuses people that’s in a different field. I remember that over five years ago, a radiologist asked me if I can mine data from the radiology system because she saw that I have Data Mining skills. I was blown away by the understanding of Data Mining to a doctor. Data Mining and data extraction is totally different. After data extraction and data preparation, data mining is used to identify patterns and relationships based on the research/business questions.
Generally speaking, due to the storage and advancement of computers, our data analysis power which builds on Statistical knowledge expanded by using more complicated statistical theory and algorithms that are applied to multidisciplinary science such as Biostatistics, Medicine, Public Health, Computer Science, Engineering, Physicis, etc.
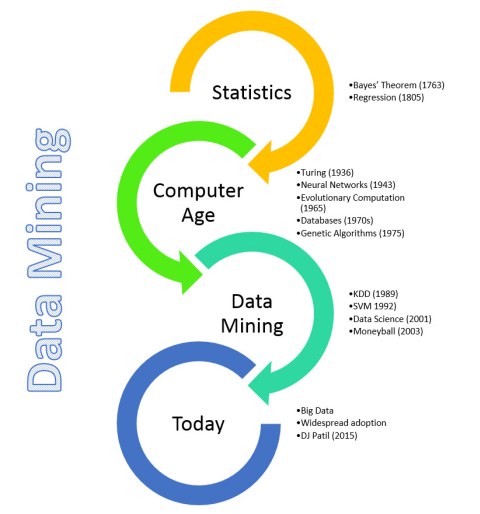
Nature has a paper “Statistics versus machine learning” that explains the relationships.From Data Mining to Knowledge Discovery in Databases discussed and summrized the history of Knowledge discovery of database (KDD).
In the realm of healthcare research studies, I would like to share my own experience of what types of statistical learning were used. Based on the objectives of a study, we generally have two types of goals:
Inference: Identify risk factors that associate with response outcome(s). It normally has smaller sample size. This is the most common goal in medical research. It requires clinical knowledge to start with research questions that involve hypothesis. Univariate analysis (Hypothesis testing) and Multivariable analysis are used. Both types of analysis need assumptions on the data distribution, variance and linear/nonlinear relationship with response variable(s) to perform correct statistical tests. For univariate analysis, please check out my slides for the most commonly used hypothesis testings. The most common problem is
significance (p-value) fishing. There are difference p-value adjustment methods to consider when there are multiple testings. Physicians/researchers often want to publish significant testing result only which is not healthy for medical research. Non significant factors are important to the literature. It’s useful for meta analysis. For multivariable analysis, here are some examples that difference statistical models were used:Clinical Outcome Study: Comparison of hospital outcomes and resource utilization in acute COPD exacerbation patients managed by teaching versus non-teaching services in a community hospital: The data was from both national database Premier and hospital EHR(Electric Health Record).
Multiple logistic regressionwas used for the multivariable analysis to identify the factors that contribute to resource utilization in the acute COPD patients.Commercial Device Study: Characterisation of ICU sleep by a commercially available activity tracker and its agreement with patient-perceived sleep quality: This data was collected from ICU patients that used fitbits as alternative sleep tracking devices. Since each patient was measured several times, a
mixed model repeated measurewas used to detect the correlation/agreement between each sleep quality measure and the gold standard Richard-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire (RCSQ). Instead of a single pearson correlation coefficient, thebootstrap methodwith 1000 times was implemented to generate Confidence Interval for statistical inference.Population Health Study: Contextual, Organizational and Ecological Effects on the Variations in Hospital Readmissions of Rural Medicare Beneficiaries in Eight Southeastern States: This a longitudinal study funded by NIH. Data was from mainly from CMS data warehouse on beneficiaries and providers. First,
risk-adjusted readmissionwas calculated by Logistic regression model on patient level. Then Generalized Estimating Equation (GEE) method was performed on the rurual clinic level for 6 years of data. This is a type ofhierarchical regression.
If the number of variables is very large compared to observations (p>n), for example genomics, a person has hundreds of genes. Or when the ratio of p/n is larger than normal and the linear/nonlinear relationships and assumptions are vague, noval machine learning methods are preferred.
One example is the breast cancer tumor classification. Another example is a Leukemia project that i’m currently working on to identify unknown gene mutation effects to the mortality of the patients. There are only 125 patients, and each patient has over 38 gene mutations. The gene mutations are sparse. Methods with penalty and constraints will be suitable for this type of data. I’ll discuss more about this project seperately later.
Prediction: Predict outcomes. It preferrs big sample size for better prediction accuracy.
- Covid 19 Study This paper was reference for prediciton: Due to the extensive research studies on Covid 19. Our hospital identified various data and interesting risk factors to predict Covid 19 positive cases. On one hand, the study aims to identify additional risk factors. and on the other hand, with over 10K patients’ data, the study aims to predict Covid 19 cases based on the massive data.
Multiple logistic regression,Random Forest, andXGboostwere used to predict the outcome. Since the risk factors and response variable have more linear relationship, and with a better interpretability,Multiple logistic regressionwith training and validation test was picked and each patient has a risk score for decision makers to utilize the hospital resources.
- Covid 19 Study This paper was reference for prediciton: Due to the extensive research studies on Covid 19. Our hospital identified various data and interesting risk factors to predict Covid 19 positive cases. On one hand, the study aims to identify additional risk factors. and on the other hand, with over 10K patients’ data, the study aims to predict Covid 19 cases based on the massive data.
Closing Note
In healthcare research, asking the right questions and have clinical knowledge is very essential to determine the patient population and appropriate methods. Understanding the problems and using the efficient methods provides a strong solution. Statistical inference is essential in traditional Health care research. Maching learning method is more flexible and is generally better for prediction, big data or unknown assumptions.